Java 코딩테스트 공부/Java 알고리즘 공부
Recursive, Tree, Graph 6 - 경로탐색(DFS, 인접리스트), 그래프 최단거리(BFS)
daramG
2023. 3. 19. 22:58
자바(Java) 알고리즘 문제풀이 입문: 코딩테스트 대비 - 인프런 | 강의
자바(Java)로 코딩테스트를 준비하시는 분을 위한 강좌입니다. 코딩테스트에서 가장 많이 출제되는 Top 10 Topic을 다루고 있습니다. 주제와 연동하여 기초문제부터 중급문제까지 단계적으로 구성
www.inflearn.com
경로탐색 (DFS)
문제1 :
방향그래프가 주어지면 1번 정점에서 N번 정점으로 가는 모든 경로의 가지 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
첫째 줄에는 정점의 수 N (1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M이 주어진다. 그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결 정보가 주어진다.
ex)

입력예제
5 9
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 1
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 2
4 5
출력예제
6
소스코드 :
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int n, m, answer = 0;
static int[][] graph;
static int[] ch;
public void DFS(int value) {
if (value == n) answer++;
else {
// 갈 수 있는 곳들로 뻗어나감
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
// 갈 수 있는 곳 && 방문하지 않은 곳
if (graph[value][i] == 1 && ch[i] == 0) {
ch[i] = 1;
DFS(i);
ch[i] = 0; // back 하고 체크 취소
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main T = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
graph = new int[n+1][n+1];
ch = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
graph[a][b] = 1;
}
ch[1] = 1;
T.DFS(1);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
한 번 방문한 노드를 재방문하면 안되므로 체크할 체크배열을 만든다.
back 이후 체크를 해제해준다.
경로탐색 (인접리스트)
만약 정점의 수가 위처럼 1<=N<=20 이 아니라 10000 정도가 주어지면 어떻게 될까?
인접행렬이 10000 x 10000이 그려질 것이고 그걸 반복문으로 돌리게 되면 엄청난 시간이 걸리게 될 것이다.
이럴때 인접리스트를 사용하면 된다.

소스코드 :
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int n, m, answer = 0;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static int[] ch;
public void DFS(int value) {
if (value == n) answer++;
else {
// 갈 수 있는 곳들로 뻗어나감
for(int nextValue : graph.get(value)) { // graph.get(value)는 value 번 ArrayList
if (ch[nextValue] == 0) {
ch[nextValue] = 1;
DFS(nextValue);
ch[nextValue] = 0; // back 하고 체크 취소
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main T = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
// 각 노드 객체 ArrayList 생성
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
ch = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
// 해당 ArrayList 원소에 접근해 추가
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
ch[1] = 1;
T.DFS(1);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
DFS 에 따라 다음 순서로 방문된다.
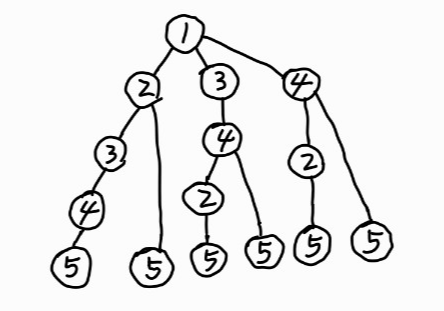

그래프 최단거리(BFS)
다음 그래프에서 1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소 이동 간선수를 출력하시오.
첫째 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M이 주어진다.
그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결정보가 주어진다.

입력예제
6 9
1 3
1 4
2 1
2 5
3 4
4 5
4 6
6 2
6 5
소스코드 :
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int n, m;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static int[] ch, dis;
public void BFS(int v) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
ch[v] = 1;
dis[v] = 0;
queue.offer(v);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cv = queue.poll();
for(int nv : graph.get(cv)) {
if (ch[nv] == 0) {
ch[nv] = 1;
queue.offer(nv);
dis[nv] = dis[cv] + 1;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main T = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
// 각 노드 객체 ArrayList 생성 (인접 리스트 생성)
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
ch = new int[n+1];
dis = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
// 해당 ArrayList 원소에 접근해 추가
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
T.BFS(1);
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
System.out.println(i+" : " + dis[i]);
}
}
}